TEAMS
> Research Interests
Our group, founded in 2014, is a team concerned with environmental issues at Shanghai Chenshan Botanical Garden. We work closely with the Montréal Botanical Garden, University of Montréal (Canada) and Institut de recherche en sciences et technologies pour l’environnement et l’agriculture (France). Our common mission is to improve the water and soil quality at urbanization area by using phytotechnology. Our research focuses on an overall better understanding of the role of macrophytes in constructed wetland system and the role of woody plants in soil decontamination, development of relevant technology and application extensively.
Four topics will be studied in our group that supported by Shanghai Administration Department of Afforestation and City Appearance. These researches are mainly included (1) management and control technology for constructed wetland systems, (2) ecological technology for low-polluted water remediation, (3) Dendroremediation of metal contaminated soil in urban area and (4) Construction theory and technology of near-natural plant community.
> Major Ongoing Projects
1. Post-evaluation for the spongy city technology of Shanghai Chenshan Botanical Garden
The monitoring results of Shanghai Chenshan Botanical Garden recreational water systems was showed that water quality could reach the III class to the IV class of the national standard of surface water quality (GB3838-2002). In according with the estimation of the amount of nitrogen and phosphorus removal, the distribution and growth of aquatic plants, the amount biomass of submerged plant, submerged plant and floating plant have been investigated. It reveal the evaluation of aquatic plant management scheme based on the control of pollutants.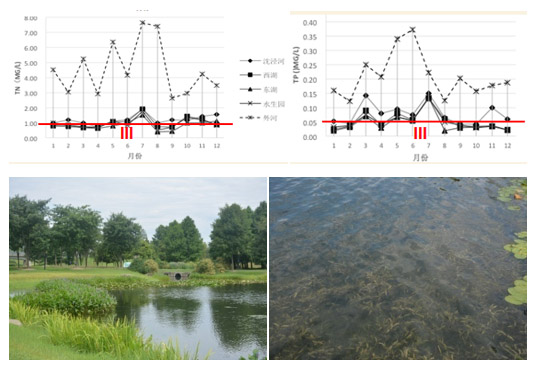
2. Plant selection and function evaluation of low-polluted water treated constructed wetland
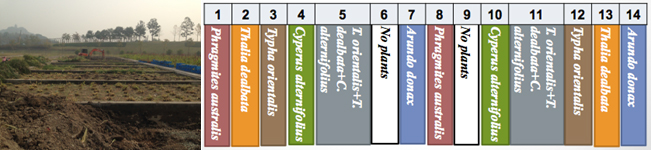
Five aquatic macrophytes plants, such as Arundo donax var. versicolor, Cyperus alternifolius, Thalia dealbata, Typha orientalis, Phragmites australias were selected and planted on gravel-type subsurface flow constructed wetlands with a length of 13 m and width of 4.5 m. The plant height, biomass, nitrogen and phosphorus content at different distance and its purification effect were conducted in this study.
The results showed that the purification effect of COD, ammonia nitrogen, total nitrogen and total phosphorus of five plant system constructed wetland was significantly better than that without plant system. With the increase of planting distance, the growth, biomass and root / shoot ratio of five plant species were showed a decreasing trend. The biomass per unit area and the accumulation of N and P were declining exponentially or logarithmically with the planting distance. The order of nitrogen removal amount by harvesting aboveground parts was: C. alternifolius > P. australias > T. dealbata > A. donax var. versicolor > T. orientalis, the phosphorus was: C. alternifolius > T. dealbata > P. australias > A. donax var. versicolor > T. orientalis. And the accumulation efficiency of N and P was P. australias > T. dealbata > C. alternifolius > A. donax var. versicolor > T. orientalis. Therefore, the plant selection for low-polluted water constructed wetland was not only focused on the high N, P accumulation species, but also should be selected with high accumulation efficiency.
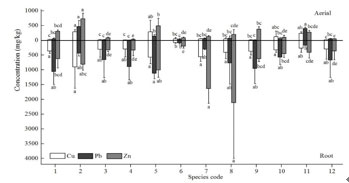
(3)Tree selection and remediation techniques in heavy metals contaminated soils
Dendroremediation is a new technology of phytoremediation. Because of its ideal characteristics such as rapid growth, large biomass, durable support, main stem, stable root and long life, woody plant can make up for the deficiency of total accumulation of hyperaccumulator. Tested by pot experiment, 13 woody plants such as Morus alba, Rhus chinensis, Chimonanthus praecox etc were candidate for Zn uptake; 12 woody plants such as Lagerstroemia indica, C. praecox, Liquidambar formosana etc were candidate for Cu uptake; 5 woody plants such as R. chinensis, C. praecox, Fraxinus chinensis etc were candidate for Pb uptake. When we select the woody plants for urban greening, a variety of ecological functions of woody including horticulture, adaptation and environmental remediation should be putted together. It could realize the city sustainable remediation of soil pollution.
Approximate order of TE removal potential was Spiraea japonica, Salix integra, Weigela florida, Euonymus japonicus, Photinia ×fraseri, Nandina domestica, Hibiscus hamabo, H. mutabilis, Cassia corymbosa estimated by TE concentrationin aerial part. However, when taken into the biomass produce, the order of total amount of TE removal was almost reversed. Woody plant species taken the same response to single-or mixed contamination. High biomass production was also very important for phytoextraction by woody plant species.
The application of Illumina Miseq sequencing platform to explore the impact of heavy metal pollution on the bacterial community in the rhizosphere soil. The experimental results showed that the soil bacteria mainly by Proteobacteria, Chloroflexi, Acidobacteria, Actinobacteria, Bacteroidetes etc. The Proteobacteria were reached in the content of soil bacteria in more than 28%.

We got the fund from Chinese and Canada government to carry out joint development of key supporting technology dendroremediation, referring to commercialization and industrialization mode of woody plant remediation technology. We will use biomass fertilizer by mulching treatment, sowing propagation of woody plants, introduced the technology of dendroremediation to adapt to the local habitat and native tree.

> Recent Publications
> Team Members
 | Principal Investigator (PI) |
Experience: In May 2014, he was appointed as the Special Advisor of the Executive President of Shanghai Chenshan Botanical Garden by the Shanghai Landscape & City Appearance Bureau of the City of Shanghai,
Activities and achievements: Through his research at the Garden and the Institut de recherche en biologievégétale (Plant Biology Research Institute), G. Vincent has become a renowned specialist in biotechnology, specifically in the use of aquatic plants for wastewater treatment. Furthermore, as director of the Garden, a position that has allowed him to combine his solid background in botany with his management skills, he has initiated and contributed to numerous special events and projects. Since May 2014, under the supervision of the executive President, he worked on the preparation of the Corporate Plan 2014-2020 of Chenshan. He is an advisor on strategic development for the departments of Horticulture, Education, Marketing and General Operation. He also led a new research in phytotechnology (Constructed wetland and Phytoremediation).
Publications and conferences: G. Vincent is author or co-author of about thirty scientific articles in peer-reviewed journals, and has given over one hundred conference presentations, both within Canada and internationally. He has published close to one hundred articles on scientific themes for the general public, and published a book on Quebec’s native flora. He has also been invited to share his scientific expertise on over 190 radio and television programs, on topics related to the environment, conservation and the role of botanical gardens in our society.
> Memberships
 | Shang Kankan |  | Zhang Guowei |
 | Kou Shumeng |  | Jacques Brisson |
 | Florent Chazarenc |  | Michel Labrecque |